Peroneal Tendonitis
Peroneal tendonitis (sometimes called peroneal tendinopathy) is a condition affecting the tendons that run along the outside of the ankle.
These tendons, known as the peroneals, pass behind the outer ankle bone and attach to the base of the fifth metatarsal (the long bone on the outside of the foot).
They play an important role in stabilising the ankle and foot, especially when walking, running, or changing direction. When the peroneal tendons are strained or overworked, they can become inflamed and painful, leading to peroneal tendonitis.
Symptoms of Peroneal Tendonitis
People with peroneal tendonitis often experience:
- Pain on the outside of the ankle or foot (commonly near the base of the fifth metatarsal)
- Swelling or tenderness around the outer ankle
- Ankle instability, particularly after an inversion injury (rolling the ankle inwards)
- Pain that worsens with activity, especially on uneven ground or when pushing up onto the toes

Common Causes
Peroneal tendonitis may occur after:
- Ankle inversion injuries (rolling the ankle inward, often mistaken for a “simple sprain”)
- Overuse — when the peroneal tendons are working too hard to stabilise the ankle during repetitive activity
- Sudden increases in training or activity levels without adequate adaptation
- Biomechanical issues such as ankle instability or high-arched feet, which place greater strain on the peroneals
Although it can affect either the left or right ankle, it is uncommon for both sides to be affected at the same time.
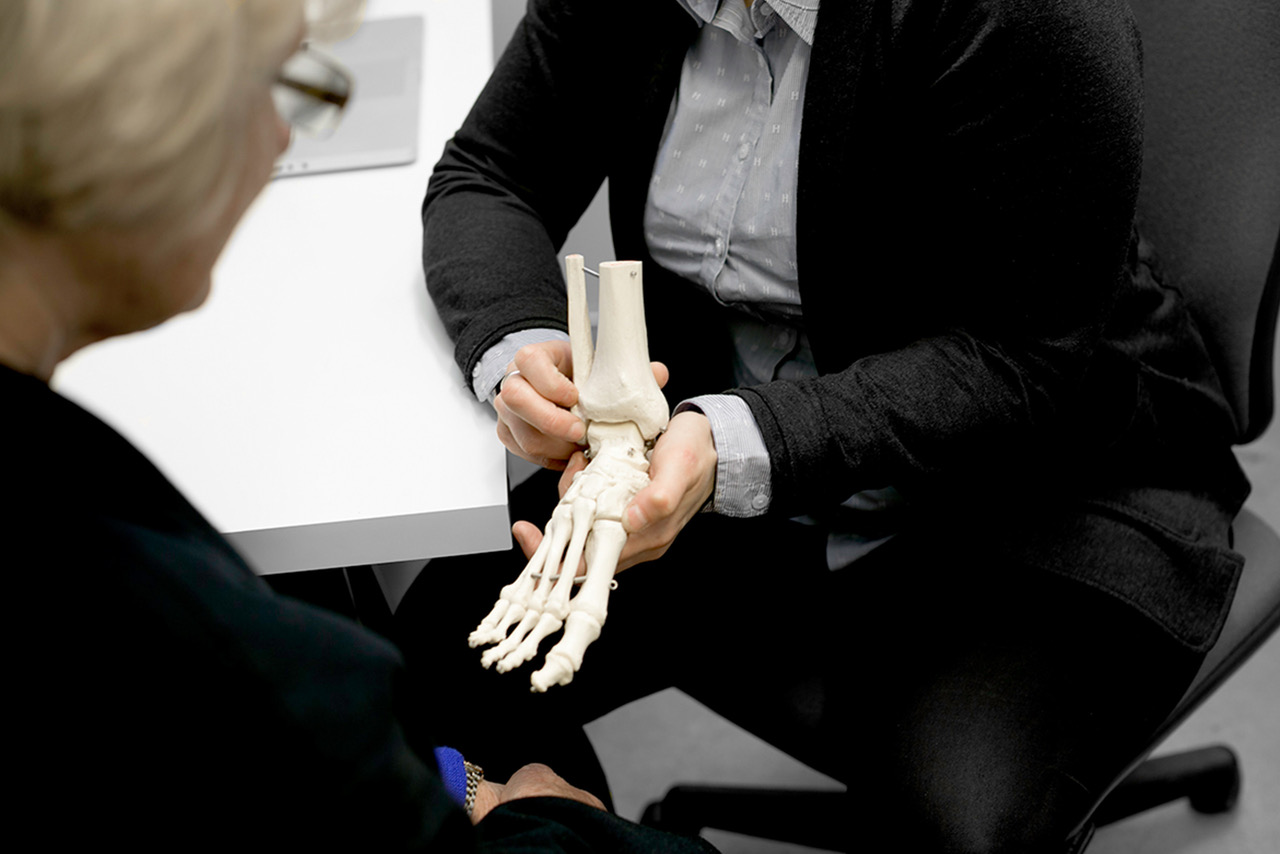
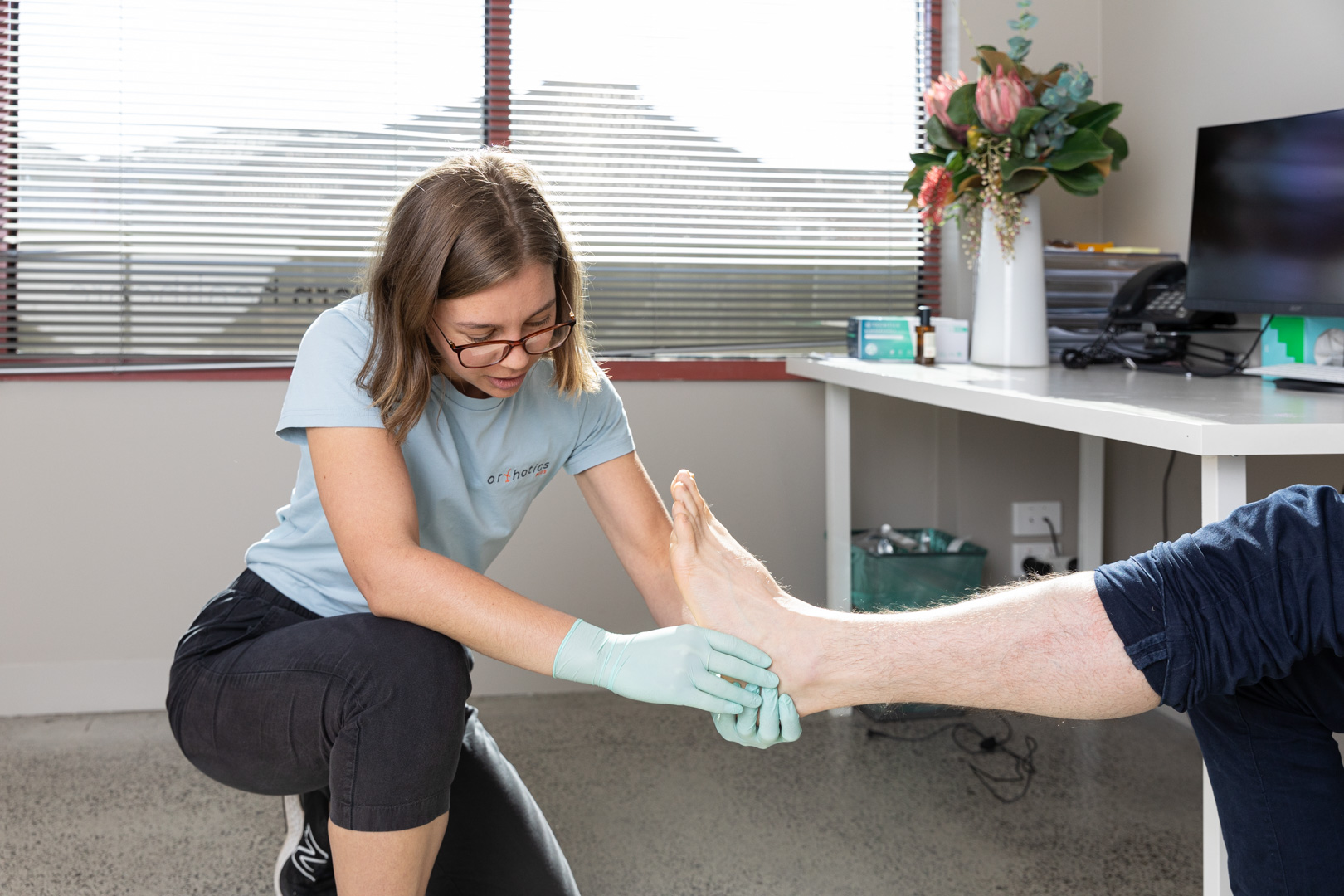
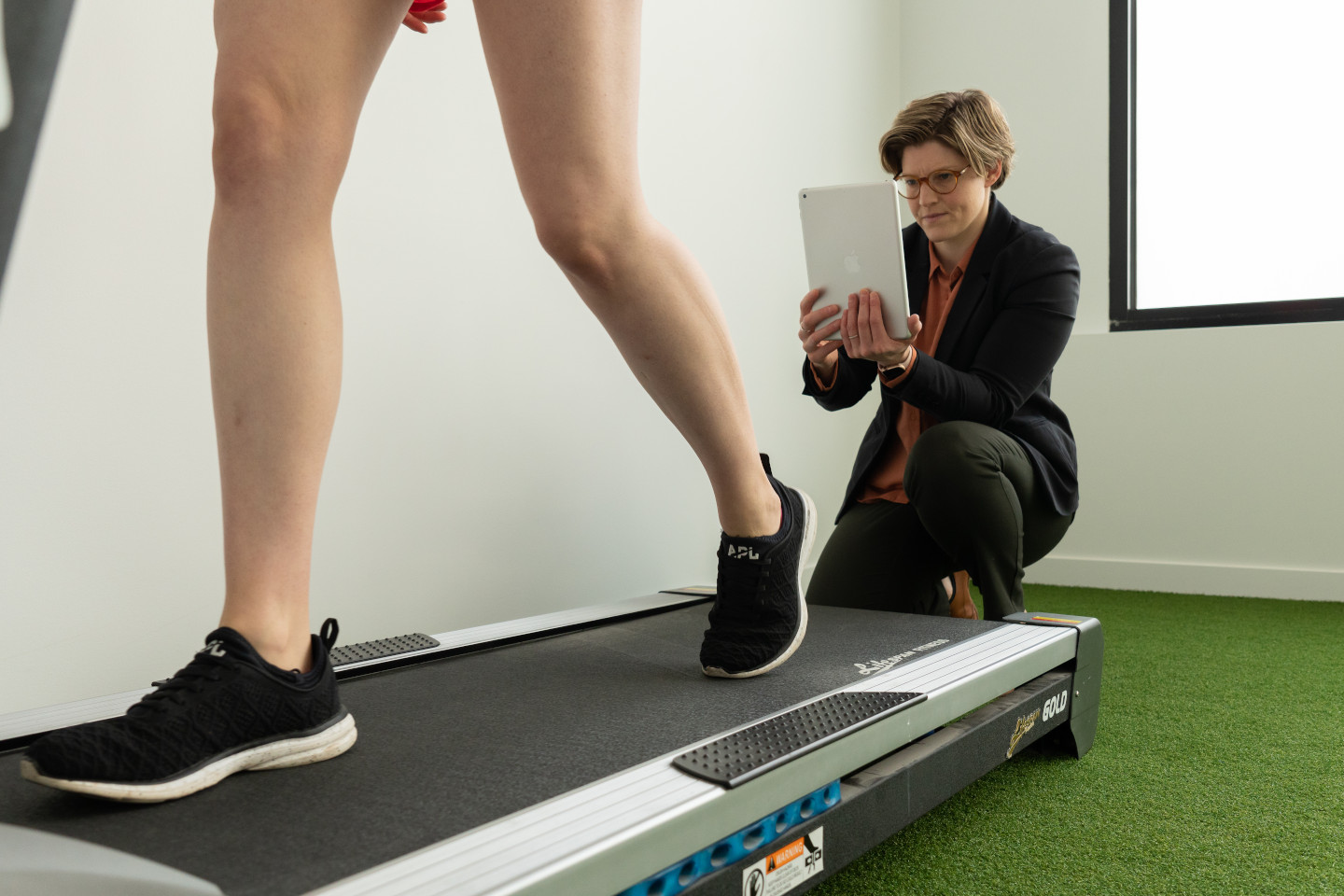
Diagnosis at Orthotics Plus
At Orthotics Plus, our clinicians conduct a thorough assessment to confirm whether a patient has peroneal tendonitis.
This begins with a detailed history, where we discuss
- the onset of pain
- how long it has been present
- any factors that make it better or worse
- and whether there have been previous injuries
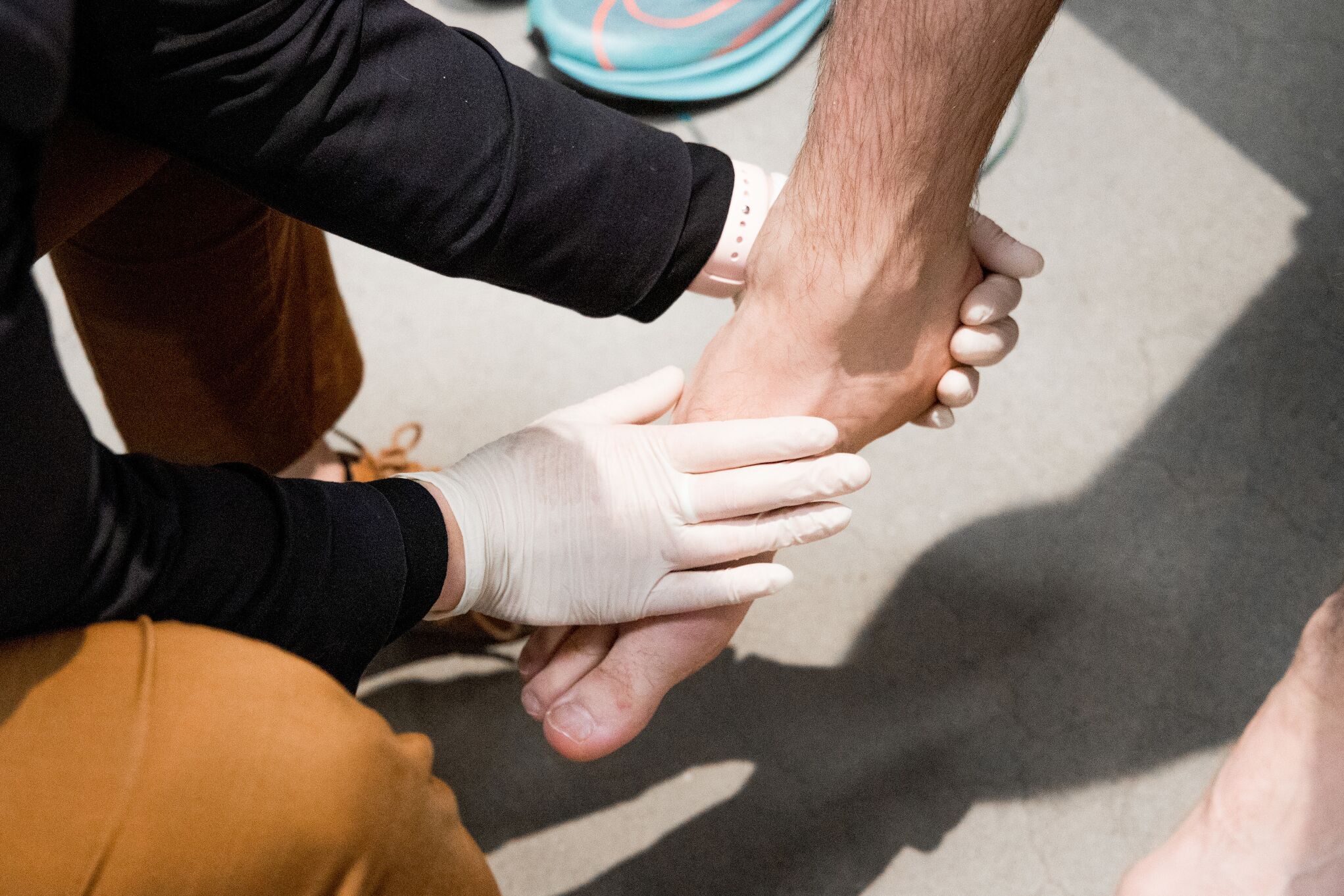
A physical examination follows, which involves palpating (gently pressing) the tendon to identify areas of tenderness, assessing ankle stability, and observing functional movements.
Using both the patient’s history and the physical findings, our clinicians apply clinical judgement to determine whether the condition is an acute injury or an overuse-related tendinopathy.
This process allows us to provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a management plan tailored to each individual.
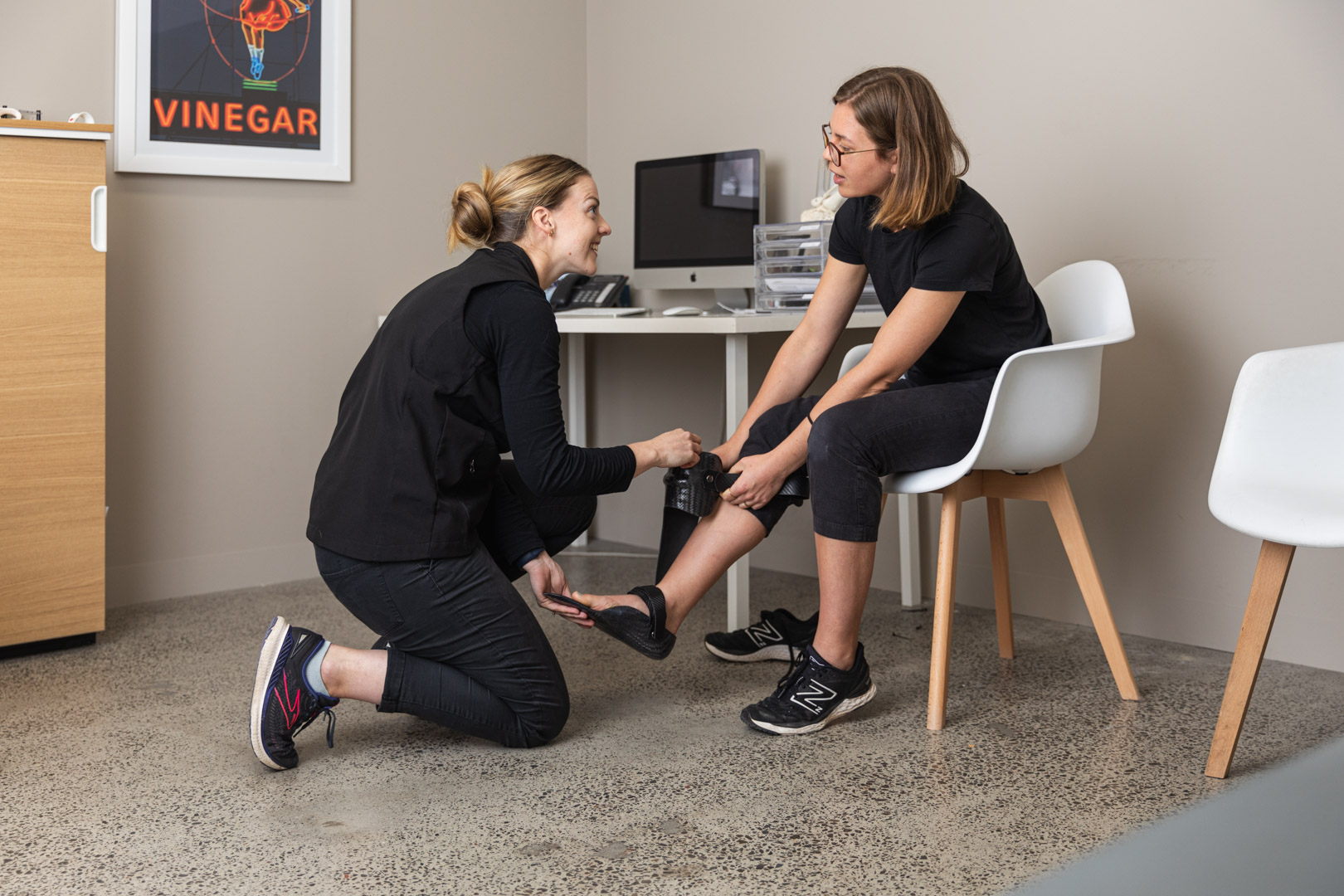
Treatment of Peroneal Tendonitis
Treatment for peroneal tendonitis is personalised, but often includes:
- Load management – reducing activity levels to allow the tendon to settle before gradually increasing load again.
- Biomechanical support – addressing contributing factors with custom foot orthotics or braces.
- ASO ankle braces – providing external stability to reduce strain on the tendon, particularly in acute cases.
- Foot orthotics – designed to stabilise the ankle, with possible modifications such as a lateral wedge to reduce outward rolling of the ankle.
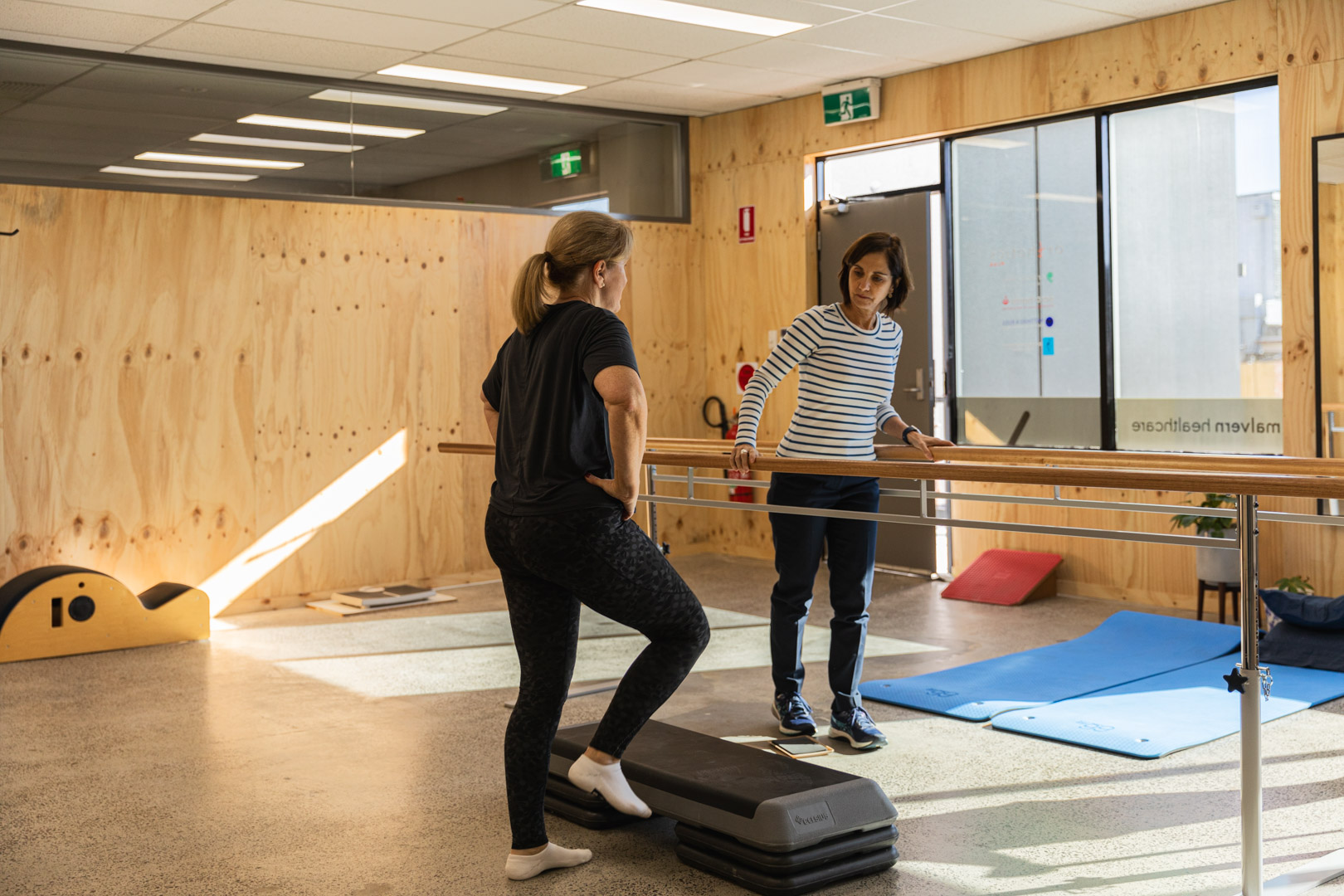
- Exercise and rehab – guided by physiotherapists, including strengthening and a graded return-to-sport program.
This process allows us to provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a management plan tailored to each individual.

Activities to Avoid During Recovery
While recovering from peroneal tendonitis, in our experience, it is usually recommended to avoid:
- Activities requiring sudden change of direction (e.g., football, basketball, netball)
- Running or sports that place strain on the toes and forefoot
- Any movements that cause pain around the ankle
A gradual, structured return-to-sport plan under physiotherapy guidance usually the way to go.

How Orthotics Plus Can Help
Our orthotists work closely with physiotherapists to support your recovery. We provide:
- Custom foot orthotics to address biomechanical causes
- ASO ankle braces for short-term stability during acute recovery
- Education on safe activity levels and progression
- Ongoing reviews to adjust orthotic devices as your ankle strengthens
If you are experiencing outer ankle pain or instability, Orthotics Plus can help assess, diagnose, and support your recovery from peroneal tendonitis.
To get started, please use our clinic locations or referrals pages.
View Clinic Locations Referrals
