How Do Orthotics Plus Help with Shoulder Braces?
We help patients who have had an acute shoulder injury with their recovery, which is primarily achieved through the use of a sling or brace.
We also help patients who have had shoulder surgery and require immobilisation for a certain period to protect the surgical site and allow that surgery to heal.
We also provide shoulder stabilising orthoses to prevent subluxation or dislocation of the glenohumeral joint due to rotator cuff weakness, following a stroke or another neurological issue. Our services are delivered to patients across our Melbourne clinics.
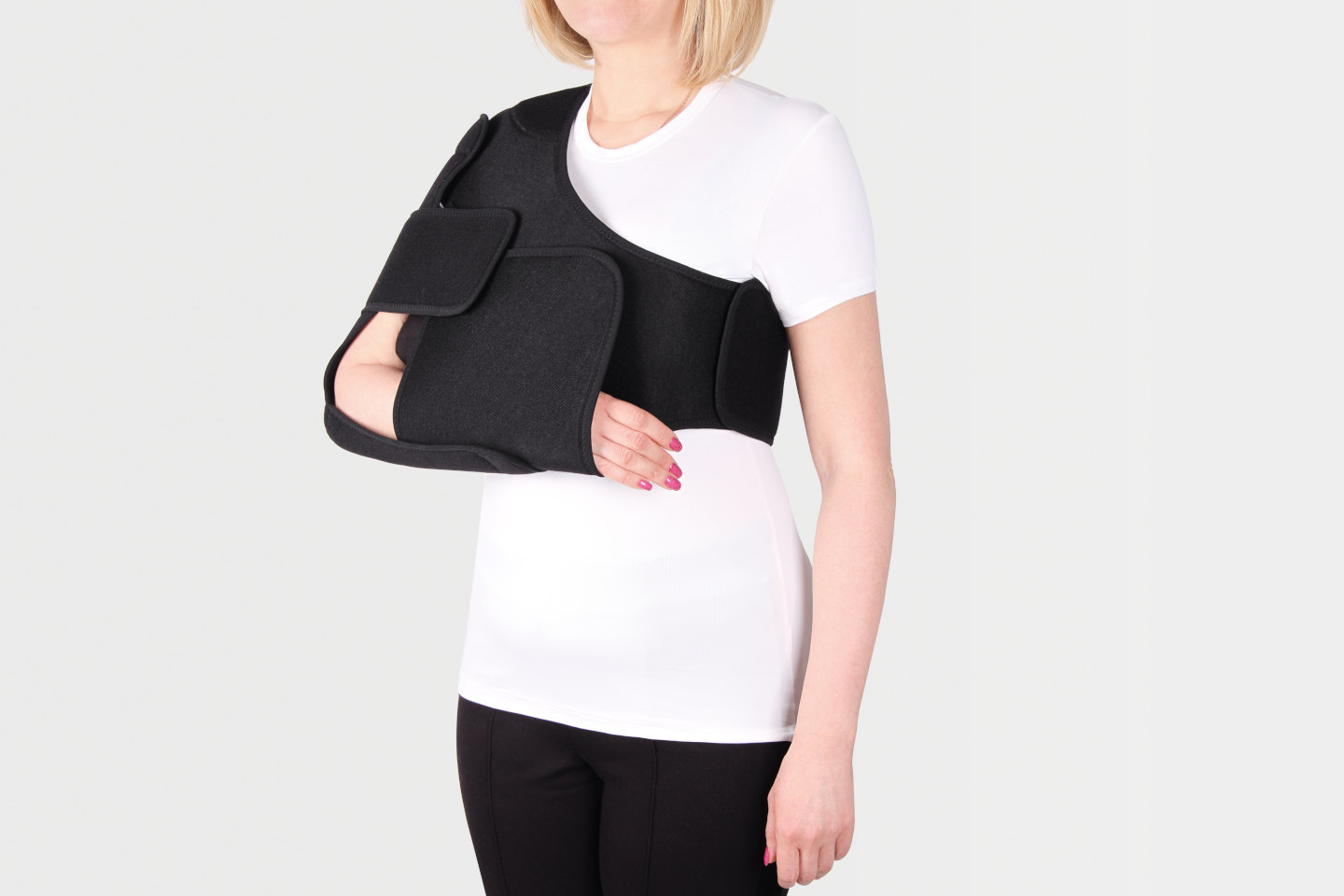

Shoulder Braces at Orthotics Plus
- Shoulder abduction sling
- Clavicle braces
- Posture support
- Paediatric arm sling
- Shoulder immobiliser
- Ossur smart sling
- Ottobock acro comfort
- Sports & injury support slings
- Ossur Innovator X Post-Op Elbow
- Humeral cast brace
- Front closure clavicle support
- Ossur FormFit Shoulder brace
- Ossur Padded strap shoulder immobiliser
- Ottobock Acro Comfort
- Omo Neurexa
- Abduction pillow
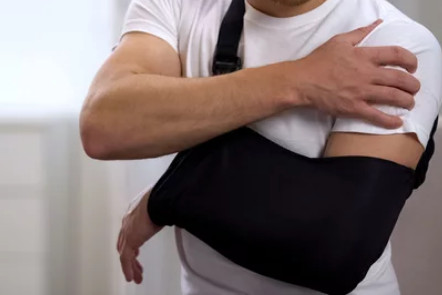
Choosing the Correct Shoulder Supports
The selection of braces must satisfy the patient’s goals and the type of injury.
Patients will visit Orthotics Plus for an assessment, treatment and recommendations. Prices of shoulder braces are highly variable, starting at approximately $60 AUD, with some high-end braces exceeding $600 AUD.
Each shoulder brace needs to be selected and carefully fitted for the individual. The patient is given choice and control.

Assessments at Orthotics Plus
Clients do not require a GP referral to start with Orthotics Plus.
However, in other cases, our patients are referred to us by their GP or surgeon. When requiring upper limb support, details of an existing diagnosis from a doctor, surgeon, or specialist are helpful.
For acute cases, we can usually assess and treat patients on the same day in the same appointment. We stock the most common equipment in-house. For custom or uncommon products, it may take us a few days to source.
Ongoing support may include follow-up appointments with our Orthotists, depending on the situation. We may also make recommendations to Allied Health professionals and any imaging that may be required.

How Are Shoulders Typically Injured?
Typically the shoulder is injured when exposed to excessive forces, excessive range of motion, or overuse.
For people living with chronic degenerative conditions, shoulder braces are typically not an appropriate strategy. Braces are more so recommended for acute rehabilitation in injury and post-surgical cases to manage pain through rehabilitation.

Request an Evaluation
Orthotics Plus is an Allied Health organisation located in Melbourne that helps the community access upper limb Orthoses including shoulder orthoses.
We are proud to employ Orthotists and Senior Orthotists with up to 25 years of experience. We are tertiary trained professionals with lots of experience treating upper limb injuries.
We will help guide you through pathways of appropriate Orthotic management, as well as refer you to other experienced professionals when necessary.

Shoulder Brace FAQ
Yes, please see our humeral fractures page for more information.
This is highly variable and will depend on the surgery, the surgeon and the patient.
Patients typically wear a shoulder brace for 2-12 weeks, this is directed by the surgeon and their protocols.
During this period you may be prescribed gentle exercises to do, with or without the shoulder orthosis. It is also common to begin wearing a sling and then gradually reduce wear as the surgery recovers and the patient rehabilitates.
As a rule, we don’t want to immobilise structures that don’t require it, so you may be able to exercise your hand and elbow while keeping the shoulder stable and protected.
The medical name for the shoulder joint is the glenohumeral joint. It is a socket joint that is composed of soft tissue, rotator cuff, ligaments and a connecting capsule.
Some textbooks describe the structure as a golf ball sitting on a golf tee, held in with small muscles and soft tissues.
The shoulder is the joint with the largest range of motion in the human body. There is a trade-off for this enhanced mobility, being that the shoulder has a lack of bony structural support.
Inherently, the shoulder is an unstable design, which is why it is the joint that dislocates the most in the human body.